Innsbruck and Aachen, 19 March 2024 – A group of physicists from ARQUE Systems and
ParityQC present a version of the ParityQC Architecture specifically for quantum
computers based on sparse grids of spin qubits. This quantum computing architecture
represents an important step forward for the advancement of spin qubits as a quantum
computing platform, efficiently harnessing their advantages such as fast timescales and
small size. This invention has been outlined in the paper “Scalable Parity Architecture
With a Shuttling-Based Spin Qubit Processor”, out now on arXiv as a pre-print.
ARQUE Systems and ParityQC have recently collaborated to develop an efficient quantum
computing architecture specific for quantum computers based on spin qubits. In the preprint
“Scalable Parity Architecture With a Shuttling-Based Spin Qubit Processor”, the
authors (Florian Ginzel, Michael Fellner, Christian Ertler, Lars R. Schreiber, Hendrik Bluhm
and Wolfgang Lechner) present the results of this joint research: a novel implementation
of the ParityQC Architecture for semiconductor spin qubits.
Among the several physical platforms for quantum computing that are currently being
investigated worldwide, one platform that has emerged is semiconductor spin qubits in
gate-defined quantum dots (QDs). ARQUE Systems, a spin-off of Forschungszentrum
Jülich and RWTH Aachen University, is currently developing and commercializing quantum
devices based on this promising platform. Spin qubits possess several important qualities
that make them a promising platform for quantum computing: they have long coherence
times, very fast gate times, a small size and a high scalability potential. In addition, the
fabrication of quantum computers based on spin qubits could be relatively easy, making
use of the sophisticated manufacturing capabilities of the semiconductor industry.
However, as with all quantum computing platforms, there are also specific challenges to
overcome, including for example environmental electric noise and cross-talk among
qubits.
These challenges represented the starting point for the collaboration between ARQUE
Systems and the quantum architecture company ParityQC. A group of physicists from the
two companies engaged in joint research, with the aim of developing architectures that
advance the use of spin qubits for quantum computing while harnessing their unique
advantages. The proposal successfully combines ARQUE’s unique approach to spin
shuttling (coherently moving the qubits in the chip on demand) with the ParityQC
framework for solving optimization problems on quantum computers.
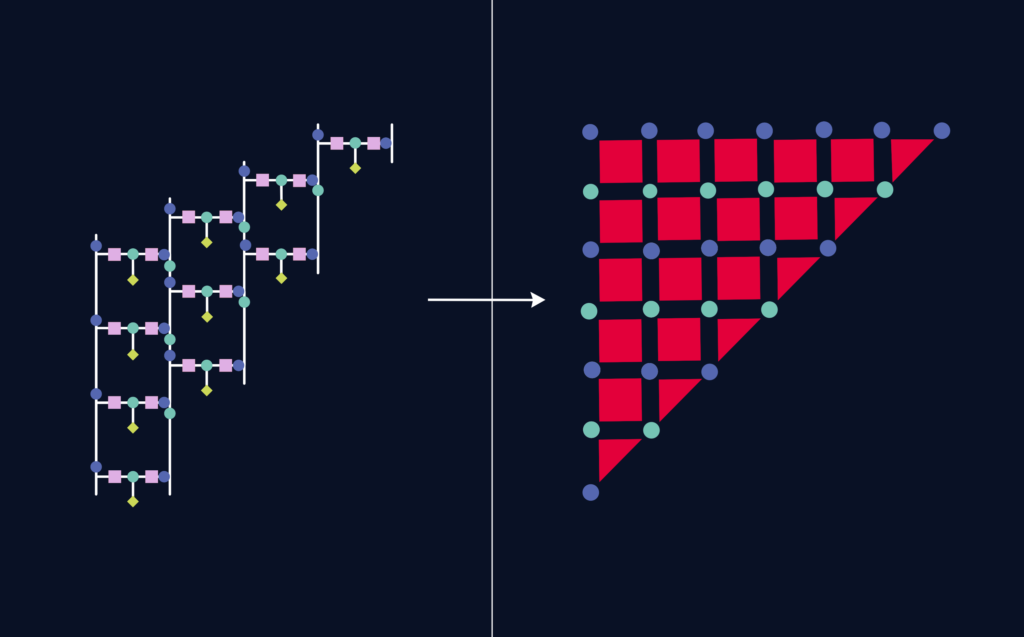
The paper explores the implementation and performance of the Parity Quantum
Approximate Optimization Algorithm – QAOA (a gate-based algorithm for solving
combinatorial optimization problems on a digital quantum computer) on two different
architectures: a sparse spin bus architecture and a modular architecture with minimal
registers. The authors develop gate sequences and an error model for each architecture
and proceed to compare the performances. Realistic errors were considered, and it was
found that both architectures can complete one round of Parity QAOA with a low singlequbit
error probability, with the spin bus architecture slightly outperforming the modular
architecture. The physical errors of both architectures were found to be low enough to
decode the final state with a high success probability, implying that the architecture has
an intrinsic potential for quantum error mitigation.
Overall, the findings in the paper represent a substantial step forward in the development
of scalable architectures for quantum computing using spin qubits, a field that has been
relatively unexplored in current literature. The research topic will continue to be explored
in the ongoing collaboration between ARQUE Systems and ParityQC, two spin-offs that
combine a strong background in fundamental research with its practical development
and commercialization.
Publication:
• Florian Ginzel, Michael Fellner, Christian Ertler, Lars R. Schreiber, Hendrik Bluhm, Wolfgang
Lechner. Scalable Parity Architecture With a Shuttling-Based Spin Qubit Processor.
arXiv:2403.09574 (2024)
About ParityQC
ParityQC is a spin-off of the University of Innsbruck and the only quantum architecture
company worldwide. The company’s focus is on developing blueprints and operating systems
for quantum computers. ParityQC collaborates with hardware partners all over the world to
jointly build quantum computers for applications ranging from solving optimization problems
on NISQ devices to general-purpose, error-corrected quantum computing.
About ARQUE Systems
ARQUE Systems is a spin-off of Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University. The
founders of ARQUE have decades of experience with semiconductor qubit technology.
ARQUE’s mission is to develop and commercialize Quantum Computing systems reaching far
beyond current capabilities based on electron spins in silicon.
Contact
Erika Bettega
Marketing & Communications
ParityQC
e.bettega@parityqc.com / +39 333 2881645